How to Choose the Right Lubrication Pump for Your Needs
Choosing the right lubrication pump is crucial for ensuring the efficient and reliable operation of machinery and equipment across various industries. A lubrication pump is designed to dispense the appropriate amount of lubricant to reduce friction and wear between moving parts, which ultimately prolongs the lifespan of both the machinery and its components. With numerous options available on the market, it can be challenging to determine which lubrication pump best suits your specific needs and operational requirements.
When selecting a lubrication pump, it is essential to consider factors such as the type of lubrication system, the viscosity of the lubricant, the operating environment, and the required flow rate. Understanding these parameters will not only help in identifying the ideal lubrication pump but also enhance overall maintenance practices. Additionally, proper assessment of the application scenario can lead to improved efficiency, reduced downtime, and optimized performance of your equipment. By keeping these considerations in mind, you can make an informed decision that results in the most effective lubrication solution for your operation.
Understanding Different Types of Lubrication Pumps in the Market
When it comes to selecting the right lubrication pump, understanding the various types available in the market is crucial. Lubrication pumps can primarily be categorized into manual, electric, and pneumatic types.
Manual pumps are often favored for their simplicity and low maintenance, making them ideal for smaller operations or equipment that doesn’t require constant lubrication. These pumps generally allow for precise control over the amount of lubricant dispensed, which can lead to improved efficiency and reduced waste.
On the other hand, electric pumps offer more automation and consistency in lubrication tasks, making them suitable for larger machinery and industrial applications. They can be equipped with timers and flow meters to ensure that the right amount of lubricant is delivered at the right intervals.
Pneumatic pumps, powered by compressed air, are also popular in industrial settings due to their ability to deliver high pressures. They are particularly effective for transferring lubricants over long distances or to multiple lubrication points simultaneously, enhancing productivity and ensuring thorough lubrication of machinery.
Understanding the specific application and operating environment is essential when choosing between these types of lubrication pumps. Factors such as viscosity of the lubricant, required flow rates, and the operational conditions must be considered. By evaluating these aspects, you can select a lubrication pump that aligns closely with your needs, ensuring optimal performance and longevity of your equipment.
Key Factors to Consider When Selecting a Lubrication Pump
When selecting a lubrication pump, several key factors come into play to ensure that you choose the right option for your specific needs. First and foremost, consider the type of lubricant you’ll be using. Different lubricants, such as grease or oil, require distinct pumping mechanisms. The viscosity and temperature of the lubricant are also critical; thicker substances may necessitate a pump with higher pressure capabilities.
Another crucial factor is the required flow rate and pressure for your application. A pump that delivers the right amount of lubricant at the right pressure will prevent insufficient lubrication, which can lead to equipment failures. Assessing the total distance the lubricant must travel and any potential obstacles in the path can also help determine the ideal pump configuration.
**Tips:** Always evaluate the physical dimensions and installation requirements of the pump to ensure it fits seamlessly into your workspace. Additionally, consider the maintenance demands; opting for a pump with lower upkeep needs can save time and resources in the long run. Finally, don’t hesitate to consult with professionals in lubrication systems to gain insights tailored to your specific application.
Lubrication Pump Selection Factors
Assessing Pump Capacity and Flow Rate Requirements for Your Application
When selecting the right lubrication pump, understanding the pump capacity and flow rate requirements for your specific application is critical. The capacity of a pump refers to the volume of lubricant it can deliver over a designated period. This measurement is essential for ensuring that the lubrication system can maintain optimal performance, avoiding both insufficient lubrication—which can lead to wear and tear on machinery—and excessive lubrication, which can result in waste and increased operational costs.
In addition to capacity, assessing the required flow rate is equally important. The flow rate is the speed at which the lubricant is delivered and is typically measured in liters per minute or gallons per minute. Different applications may require varying flow rates based on factors such as machinery size, type, and operating conditions. For instance, high-speed equipment may necessitate a higher flow rate to ensure consistent lubrication, while slower operating machinery might operate effectively with a lower flow rate. Understanding these parameters will allow you to choose a lubrication pump that meets both the technical demands of your machinery and the efficiency goals of your operation.
Evaluating the Lubrication Pump Materials and Construction Standards
When selecting a lubrication pump, the materials and construction standards play a pivotal role in ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Pumps are typically constructed from various materials such as stainless steel, aluminum, and plastic, each offering distinct advantages. Stainless steel, for example, is renowned for its corrosion resistance and strength, making it suitable for harsh environments. In contrast, aluminum can provide a lighter weight solution with good durability, while plastic options may be more appropriate for lighter applications where cost-effectiveness is a priority.
In evaluating the construction standards, it's essential to consider certifications and industry benchmarks that demonstrate a pump's reliability and safety. Pumps designed to adhere to international standards, such as ISO or API, are likely to meet rigorous testing and performance criteria. Additionally, examining the design elements such as seals, fittings, and valves can reveal the pump's suitability for specific lubricants and operational conditions. By focusing on materials and construction standards, you can ensure that the lubrication pump selected will meet your specific operational needs while minimizing the risk of premature failure or maintenance issues.
Cost Analysis: Budgeting for Initial Purchase and Maintenance of Pumps
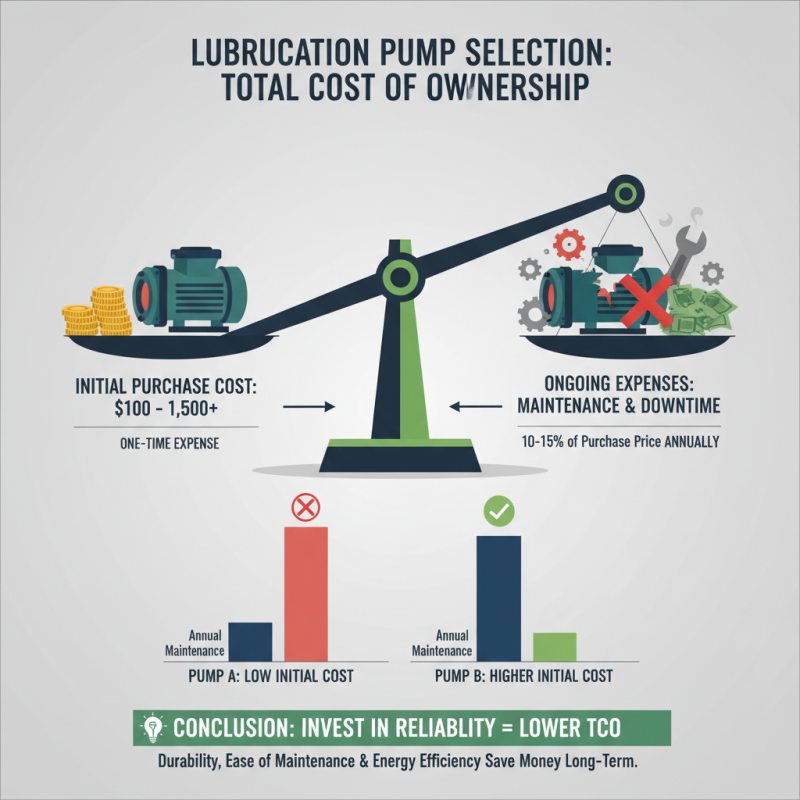
When selecting a lubrication pump, it's essential to evaluate not only the performance specifications but also the financial implications of your choice. According to the "Global Lubrication Pumps Market" report by Industry Research, the initial purchase cost of lubrication pumps can range from $100 to over $1,500, depending on the type and features. This purchase decision sets the stage for ongoing expenses, particularly in terms of maintenance and operational efficiency. Poorly maintained pumps can lead to increased downtime and costly repairs, with maintenance costs averaging about 10-15% of the original purchase price annually.
Furthermore, energy consumption is a crucial factor in the total cost of ownership. According to the "Energy Efficiency in Industrial Lubrication Systems" report, lubrication pumps can account for a significant portion of energy usage in manufacturing plants, sometimes exceeding 30% of total mechanical energy consumption. Investing in a high-efficiency pump may have a higher upfront cost; however, it can yield savings in energy bills that contribute to a lower total expense over the pump's lifecycle. An accurate cost analysis that includes both upfront and ongoing expenses will guide you in selecting a lubrication pump that meets your operational needs while staying within budget.
Related Posts
-
The Essential Role of Lubrication Pumps in Enhancing Equipment Lifespan and Efficiency
-

How to Choose the Right Pumps for Oil Based on Your Specific Needs
-

Top 5 Positive Displacement Pump Manufacturers You Should Know About
-
Understanding the Impact of Oil Lubrication Pumps on Equipment Longevity: Key Insights and Data
-

How to Choose the Right Type of Industrial Pump for Your Application
-

Understanding the Benefits of Screw Pumps in Modern Industrial Applications