What is a Crude Oil Pump and How Does It Work?
Crude oil pumps play a crucial role in the oil and gas industry. These pumps are responsible for transporting crude oil from extraction sites to refineries. According to the International Energy Agency, global oil demand is projected to reach 104 million barrels per day by 2026. This growing demand drives the need for efficient crude oil pumps.
Experts emphasize the importance of reliability in pumping systems. John Smith, a leading engineer in this field, stated, "The efficiency of crude oil pumps directly affects production output." His observations highlight how a slight failure can lead to significant losses. In this industry, each component must operate seamlessly to avoid costly downtimes.
Yet, the industry faces challenges. Aging infrastructure and fluctuating oil prices create obstacles. Many companies must assess their pumping technologies regularly. Investing in modern pumps can enhance overall efficiency. It’s essential that operators understand both the benefits and limitations of their systems. Balancing innovation with practical applications can lead to more sustainable practices in crude oil extraction.

Understanding the Function of a Crude Oil Pump
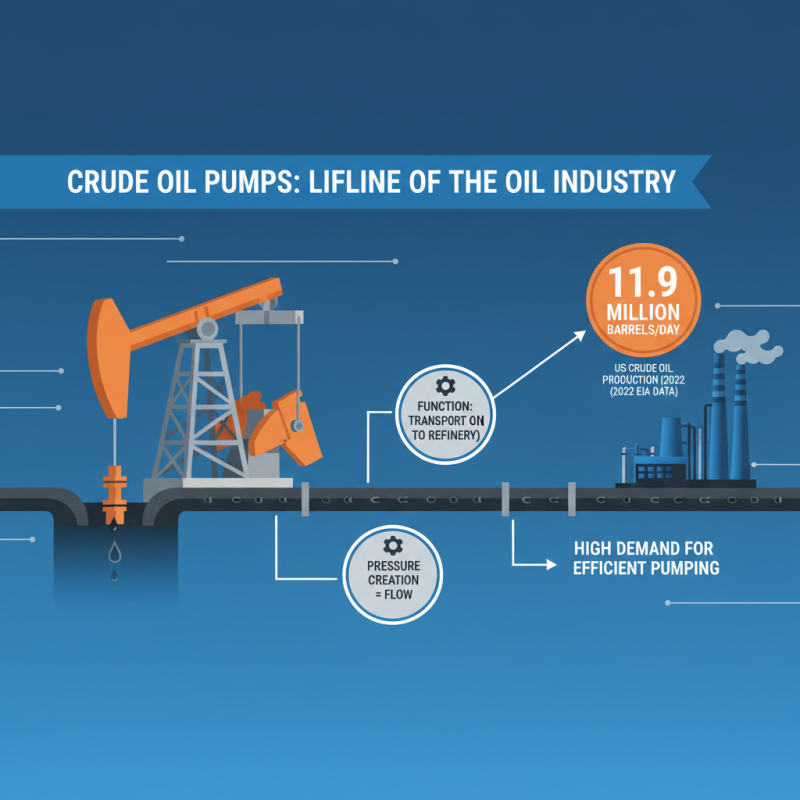
A crude oil pump plays a vital role in the oil industry. Its main function is to transport crude oil from production sites to refineries. By creating the necessary pressure, it facilitates the flow of oil through pipelines, making it an essential component of the oil supply chain. According to the Energy Information Administration, in 2022, U.S. crude oil production reached a daily average of 11.9 million barrels. This highlights the demand for efficient pumping systems.
Understanding how a crude oil pump operates is crucial. These pumps can be positive displacement or centrifugal types. Positive displacement pumps trap a fixed amount of oil and forces it into the pipeline. In contrast, centrifugal pumps use rotational energy to move the oil. Each type has its advantages and specific applications in oil transport. Adjustments in pump settings can significantly impact efficiency. Regular maintenance is essential to ensure optimal performance.
**Tips:** Regularly inspect pumps for wear and tear. Preventive maintenance can save costs in the long run. Monitor pressure levels closely to avoid pipeline ruptures. Additionally, consider the environmental impact of pumping operations. Sustainable practices are increasingly important as the industry evolves. Monitoring emissions and reducing waste can enhance the overall system performance and compliance.
Types of Crude Oil Pumps and Their Applications
Crude oil pumps play a vital role in the oil industry. Various types cater to different applications. Centrifugal pumps are common, especially for transporting oil over long distances. They are efficient and reliable. Positive displacement pumps are another type. These pumps work by moving oil using mechanical devices, providing consistent flow rates.
Certain types of pumps are better for specific tasks. For instance, gear pumps are ideal for thick oils. They deliver high pressure but may consume more energy. Progressive cavity pumps are well-suited for transferring heavy, viscous crude oil due to their gentle handling.
Tips: Always consider the viscosity of crude oil when selecting a pump. An inappropriate choice may lead to inefficiencies or even damage. Regular maintenance is crucial; wear and tear can affect performance significantly. Monitoring fluid characteristics can enhance pump lifespan. Remember to revisit your selection as conditions change.
The Working Mechanism of Crude Oil Pumps
Crude oil pumps play a critical role in the oil and gas industry. They are machines designed to move crude oil from extraction sites to refineries. The working mechanism of these pumps can be complex but essential for maintaining flow rates and pressure levels. A typical crude oil pump system may utilize centrifugal or positive displacement pumps.
Centrifugal pumps use rotational motion to lift crude oil. They can handle large volumes but may struggle with highly viscous fluids, causing potential flow issues. In contrast, positive displacement pumps work by trapping fixed amounts of oil and forcing them through the discharge. This method provides consistent flow regardless of the oil's viscosity, making it a preferred choice in certain applications. Data from the industry's market reports indicate that around 40% of global crude oil production relies on positive displacement technology to ensure efficiency and reliability.
Despite these advancements, issues such as wear and tear, pump failures, and maintenance challenges persist. A study conducted by the American Petroleum Institute found that nearly 30% of pump failures result from insufficient lubrication. Operators must regularly monitor and maintain their equipment to prevent unexpected downtime. The effectiveness of a crude oil pump system can significantly impact operational costs and production efficiency, emphasizing the need for proper management practices in an already complex sector.
Key Components of a Crude Oil Pump Explained
Crude oil pumps play a vital role in the oil industry. Understanding their key components helps to grasp how they function. At the heart of a crude oil pump is the motor, which provides the energy needed for operation. This motor is often coupled with a drive shaft. The shaft turns the pump impeller, creating the necessary suction to draw oil.
Another significant component is the casing, which houses the impeller. The casing is designed to withstand high pressure, ensuring that the oil flows smoothly. Additionally, seals and bearings help maintain efficiency. According to the Research Institute for Petroleum Technology, poor sealing can lead to a 5% loss in efficiency.
Moreover, valves control the flow of oil. These are essential for managing pressure and preventing backflow. Regular maintenance of these components is crucial. Data indicates that 30% of failures in pumps are due to improper maintenance. Operators must remain vigilant. A small oversight can result in operational inefficiencies and increased costs. It's a constant balance of monitoring and responding to changing conditions in production.
Crude Oil Pump Efficiency by Type
Maintenance and Efficiency Considerations for Crude Oil Pumps
Crude oil pumps are vital in the oil extraction and transportation process. Their efficiency depends heavily on regular maintenance. Routine checks can help identify issues like leaks or unusual vibrations. These problems, if ignored, lead to costly breakdowns. Scheduled maintenance prevents unexpected downtime.
Temperature and pressure settings are crucial for optimal performance. Pumps operate best within specific ranges. If these limits are exceeded, inefficiencies arise. Systematic monitoring helps maintain these parameters. Some operators overlook this aspect, causing decreased efficiency over time. Proper training and awareness among staff are important for consistent performance.
Using quality materials can enhance pump life. However, the initial investment may be higher. Not all maintenance practices are equal, and some methods may not yield expected results. Reflecting on past experiences can lead to better strategies. A holistic approach ensures pumps run smoothly and efficiently. Regular audits of maintenance practices can help maintain high operational standards.
Related Posts
-

Top 10 Essential Pumps for Oil: Your Ultimate Buying Guide
-
Why You Should Choose Air Oil Pumps for Your Industrial Needs Today
-

Top 10 Pumps for Oil to Maximize Efficiency and Performance
-

How to Choose the Right Pumps for Oil Based on Your Specific Needs
-

Innovative Trends in Oil Pumping Machines at the 138th Canton Fair 2025 in China
-
The Essential Role of Lubrication Pumps in Enhancing Equipment Lifespan and Efficiency