What is a High Pressure Positive Displacement Pump and How It Works in Industrial Applications
In the ever-evolving landscape of industrial applications, the high pressure positive displacement pump stands out as a critical component for numerous sectors, including oil and gas, pharmaceuticals, and chemical processing. According to a recent report by MarketsandMarkets, the global positive displacement pump market is projected to reach USD 12.3 billion by 2025, driven by the growing demand for efficient fluid handling solutions in high-pressure environments. This pump type not only ensures reliable fluid transfer but also provides precise flow rates, making it indispensable for industries where accuracy and efficiency are paramount.
Dr. John Smith, a leading expert in fluid dynamics and author of numerous publications on industrial pumps, emphasizes the significance of understanding how these pumps operate:
"The high pressure positive displacement pump is not merely a tool; it represents a fundamental technology that enhances production efficiency while minimizing waste."His insight reflects the critical role of such pumps in optimizing operational workflows and maintaining cost-effectiveness within industrial settings. As the market continues to expand and innovate, understanding the mechanics and applications of high pressure positive displacement pumps becomes increasingly essential for industry professionals seeking to stay competitive in their fields.
Understanding High Pressure Positive Displacement Pumps: Key Features and Benefits
High pressure positive displacement pumps (HPPDPs) are crucial in various industrial applications due to their ability to deliver fluids at high pressures with precise control. These pumps operate by trapping a fixed amount of fluid and forcing it through the discharge pipe, making them ideal for applications requiring consistent flow rates under varying pressures. According to a recent market analysis by Research and Markets, the global positive displacement pump market is projected to grow to $18.75 billion by 2026, highlighting the increasing reliance on these pumps in sectors such as oil and gas, pharmaceuticals, and wastewater treatment.
One of the key features of HPPDPs is their ability to handle high-viscosity fluids, making them suitable for applications in industries like food and beverage, where thick substances need to be transported efficiently. An important benefit is their lower risk of cavitation compared to centrifugal pumps, resulting in enhanced reliability and reduced maintenance costs. Moreover, these pumps can operate efficiently across a wide range of flow rates, adapting to demand without sacrificing performance, which can significantly optimize process efficiency.
**Tip:** When selecting a high pressure positive displacement pump, consider the fluid characteristics and required flow rates to ensure optimal performance. Additionally, regular maintenance checks can prolong the lifespan of the pump and prevent costly downtimes.
Mechanisms of Operation: How High Pressure Positive Displacement Pumps Work
High pressure positive displacement pumps are essential in various industrial applications due to their ability to move liquids at very high pressures. These pumps operate on a principle where a fixed amount of fluid is displaced with each cycle of movement, allowing for consistent and accurate flow rates. The mechanism typically involves a chamber that expands and contracts, utilizing pistons or gear systems to push the fluid through the discharge outlet. This unique operation is particularly beneficial in processes requiring precise dosing or where high viscosity fluids must be transferred.
Tip: When selecting a high pressure positive displacement pump, consider the fluid's properties such as viscosity and temperature. This will ensure optimal pump performance and longevity.
In addition to their efficiency, these pumps can handle a wide range of fluids, from water to more viscous materials like oils or slurries. Understanding the specific requirements of your application will help you choose the right pump type, whether it's a gear, diaphragm, or screw pump. Regular maintenance and monitoring are crucial to maintain their performance and prevent any potential issues related to wear or pressure fluctuations.
Tip: Always refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines for maintenance schedules and operational limits to avoid premature wear and ensure reliable performance in high-pressure scenarios.
Applications in Industry: Common Uses and Advantages of These Pumps
 High pressure positive displacement pumps are integral to various industrial applications due to their ability to transport fluids efficiently under high pressures. These pumps work by trapping a fixed amount of fluid and forcing it through the discharge pipe, making them ideal for moving viscous fluids or handling varying flow rates. In industries such as oil and gas, chemical processing, and food production, their reliability and consistency are essential for maintaining operational efficiency and ensuring system integrity.
High pressure positive displacement pumps are integral to various industrial applications due to their ability to transport fluids efficiently under high pressures. These pumps work by trapping a fixed amount of fluid and forcing it through the discharge pipe, making them ideal for moving viscous fluids or handling varying flow rates. In industries such as oil and gas, chemical processing, and food production, their reliability and consistency are essential for maintaining operational efficiency and ensuring system integrity.
One of the primary advantages of high pressure positive displacement pumps is their capability to deliver high flow rates at substantial pressures, which is essential in applications such as hydraulic systems and water treatment processes. Additionally, they can handle a broad range of fluids, including slurries and foam, without significant performance loss. Their robust design ensures durability and longevity, making them a cost-effective solution for industries that demand high performance and low maintenance. By leveraging these pumps, industrial operators can enhance production capabilities while minimizing downtime and operational risks.
Maintenance Best Practices for High Pressure Positive Displacement Pumps
Maintenance is crucial for the optimal performance of high pressure positive displacement pumps in industrial applications. Regular inspections can prevent unexpected failures and prolong the pump's lifespan. Operators should routinely check for leaks, unusual noises, and vibrations that may indicate wear or malfunction. Monitoring fluid levels and reviewing operating conditions also play a significant role in identifying potential issues early.
Another best practice is to follow a structured maintenance schedule, which includes replacing filters and seals as necessary. The lubrication system should be regularly checked to ensure that all moving parts are adequately lubricated, reducing friction and wear. Additionally, staff should be trained to understand the specific requirements and operational limits of the pump to avoid operating it beyond its designated capacity, which can lead to premature failure. Implementing these best practices can significantly enhance the reliability and efficiency of high pressure positive displacement pumps in industrial settings.
Comparative Analysis: High Pressure Positive Displacement Pumps vs. Other Pump Types
High pressure positive displacement pumps (HPPDPs) are renowned for their ability to generate high pressures with minimal flow variation, making them indispensable in various industrial applications. Unlike centrifugal pumps, which rely on velocity and kinetic energy to move fluids, HPPDPs operate by trapping a fixed volume of fluid and forcing it through the discharge. This fundamental mechanism provides strong advantages in scenarios requiring precise flow control and high viscosity fluid transfer.
When comparing HPPDPs to other pump types, such as centrifugal or gear pumps, it is crucial to consider efficiency and maintenance. While centrifugal pumps excel in low-viscosity applications with high flow rates, they struggle under back pressure conditions. HPPDPs, with their ability to handle highly viscous fluids and deliver consistent pressure, outperform them in demanding setups. Additionally, gear pumps are efficient for certain industrial applications but may require more maintenance due to wear on internal components.
**Tips:** When selecting a pump for your application, assess the fluid's viscosity and required pressure. Ensure that the chosen pump type aligns with your system's operational demands to optimize performance and reduce maintenance costs. Regularly monitor pump operation to detect any deviations early, ensuring longevity and reliability in your processes.
Comparative Analysis: High Pressure Positive Displacement Pumps vs. Other Pump Types
| Pump Type | Flow Rate (GPM) | Pressure (psi) | Efficiency (%) | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High Pressure Positive Displacement Pump | 5 - 50 | 1000 - 5000 | 85 - 95 | Chemical processing, Oil and gas, Water treatment |
| Centrifugal Pump | 10 - 1000 | 30 - 150 | 60 - 80 | Water supply, HVAC systems, Irrigation |
| Diaphragm Pump | 1 - 30 | 100 - 300 | 70 - 90 | Food processing, Pharmaceuticals, Wastewater |
| Gear Pump | 0.5 - 500 | 50 - 1500 | 75 - 90 | Hydraulic systems, Fuel oil transfer, Lubrication |
Related Posts
-

Exploring the Surge of Rotary Positive Displacement Pumps: Insights from the 2025 China Import and Export Fair
-

Exploring the Different Types of Positive Displacement Pumps for Optimized Fluid Transfer
-

Top 5 Positive Displacement Pump Manufacturers You Should Know About
-
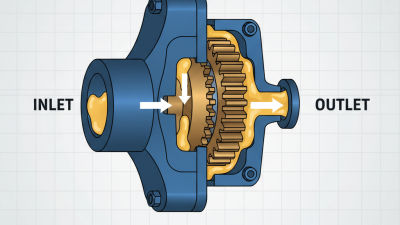
Understanding the Mechanism of Lube Pumps: A Comprehensive Guide for Efficient Lubrication Systems
-

How to Maximize Efficiency with Screw Pumps in Industrial Applications
-

How to Choose the Right Type of Industrial Pump for Your Application