Top 10 Pumps for Oil to Maximize Efficiency and Performance
In the ever-evolving landscape of the oil industry, the efficiency and performance of operations hinge significantly on the equipment employed. Among the myriad tools available, pumps for oil stand out as essential components that facilitate the smooth transfer and management of fluids in various applications. The right selection of pumps can lead to significant enhancements in productivity, reduced downtime, and overall cost savings.
As oil extraction and processing become more complex, choosing the appropriate pump type becomes crucial. The efficiency of pumps for oil not only affects operational performance but also has a substantial impact on environmental sustainability by minimizing spills and reducing energy consumption. Therefore, it becomes imperative for industry stakeholders to stay informed about the latest advancements and innovations that can optimize these vital systems.
In this article, we will explore the top 10 pumps for oil, focusing on their features, capabilities, and applications. By understanding the strengths and limitations of these pumps, operators can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals, ultimately leading to enhanced efficiency and performance across the board.

Overview of Oil Pumps and Their Importance in the Industry
Oil pumps play a critical role in the petroleum industry, serving as essential equipment for the efficient transportation and processing of crude oil and its derivatives. According to the International Energy Agency, the demand for oil globally is projected to reach 104 million barrels per day by 2025, making the reliability and efficiency of oil pumps more crucial than ever. These pumps are responsible for moving oil from the ground through complex systems of pipelines and refineries. Their operational efficiency impacts not only production costs but also the overall sustainability of oil operations, as lost energy in pump systems can lead to significant waste and environmental concerns.
In recent studies, it has been observed that advancements in pump technology, such as the integration of smart sensors and automation capabilities, can enhance performance and reduce operational downtime. The American Society of Mechanical Engineers highlights that modern pumps, when maintained and operated correctly, can achieve efficiencies exceeding 90%, translating into considerable cost savings over time. Additionally, by using predictive maintenance strategies, companies can significantly extend the lifespan of their pumps, thereby maximizing return on investment and reducing the environmental footprint associated with oil extraction and processing. As the industry evolves towards more efficient practices, the importance of selecting the right oil pump cannot be overstated.
Key Features to Consider When Selecting Oil Pumps
When selecting oil pumps, understanding the key features that impact both efficiency and performance is essential. One of the most critical factors to consider is the pump's displacement and flow rate. A pump with a suitable displacement will ensure that the desired volume of oil can be moved efficiently, minimizing energy consumption while maintaining operational effectiveness. Additionally, the flow rate should align with the specific requirements of the application to prevent any bottlenecks or energy losses.
Another important aspect is the pump's construction materials and design. Pumps that are made from durable materials can withstand the corrosive nature of oil, prolonging their lifespan and reducing maintenance costs. Furthermore, the design should facilitate ease of installation and maintenance — features like a modular design or accessible components can significantly enhance user convenience. Lastly, it's crucial to evaluate the pump's compatibility with various types of oils, as different applications may require specific performance characteristics. By focusing on these key features, one can select an oil pump that not only meets operational demands but also maximizes overall efficiency in the long run.
Top 10 Pumps for Oil to Maximize Efficiency and Performance - Key Features to Consider When Selecting Oil Pumps
| Pump Model | Flow Rate (GPM) | Max Pressure (PSI) | Power Source | Material | Weight (lbs) | Efficiency Rating |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model A | 20 | 150 | Electric | Cast Iron | 75 | 85% |
| Model B | 15 | 200 | Diesel | Aluminum | 60 | 90% |
| Model C | 25 | 100 | Electric | Stainless Steel | 80 | 92% |
| Model D | 30 | 180 | Gasoline | Plastic | 55 | 88% |
| Model E | 18 | 160 | Electric | Bronze | 70 | 84% |
| Model F | 22 | 140 | Solar | Composite | 65 | 91% |
| Model G | 27 | 220 | Electric | Cast Iron | 90 | 87% |
| Model H | 19 | 175 | Hydraulic | Aluminum | 50 | 93% |
| Model I | 24 | 190 | Electric | Stainless Steel | 85 | 86% |
| Model J | 23 | 160 | Gasoline | Plastic | 75 | 89% |
Top 10 Oil Pumps Recommended for Efficiency and Performance
When it comes to optimizing efficiency and performance in oil transfer and management, selecting the right pump is crucial. According to a recent report by the American Petroleum Institute, the global oil and gas industry is projected to grow at a CAGR of 4.2% from 2023 to 2030. As operations scale up, the demand for high-efficiency pumps that minimize energy consumption and reduce operational costs becomes increasingly important. A study conducted by the Hydraulic Institute reveals that poor pump selection can lead to energy losses of up to 30%, highlighting the critical need to invest in pumps specifically designed for oil applications.
High-performance oil pumps not only enhance fluid transfer efficiency but also contribute to the overall longevity of oil drilling and production equipment. The efficiency of pumps is often measured by their hydraulic performance, with standard benchmarks indicating that well-designed pumps can achieve efficiencies above 85%. Moreover, the use of advanced materials and technologies, such as wear-resistant coatings and smart sensors, can significantly increase a pump's reliability and reduce maintenance needs. Data from the International Energy Agency suggests that implementing more efficient pumping systems could yield an estimated savings of up to $6 billion annually in energy costs across the industry, making it an economically sound investment for operators aiming to boost their performance in a competitive market.
Top 10 Oil Pumps for Efficiency and Performance
This bar chart displays the efficiency (in %), flow rate (in L/min), and performance ratings of the top 10 oil pumps, allowing users to compare options easily.
Comparative Analysis of Pump Types for Various Oil Applications
When it comes to pumping oil efficiently across various applications, selecting the right type of pump is crucial for maximizing both performance and operational efficiency. Different oil applications, such as upstream exploration, midstream transportation, and downstream refining, present unique requirements that must be addressed. For instance, positive displacement pumps are often used in upstream operations where high viscosity is common, providing a strong suction and a consistent flow rate. Conversely, centrifugal pumps are frequently favored for their efficiency in transporting low-viscosity oils over long distances, allowing for higher flow rates needed in midstream processes.
Additionally, the choice of pump type can also be influenced by factors such as the specific characteristics of the oil being pumped, including temperature and pressure conditions. For example, high-temperature applications may require specialized pumps made from advanced materials to withstand thermal stress, while low-temperature situations might necessitate pumps designed to handle waxy crude or minimize viscosity changes.
Furthermore, considerations around energy consumption and maintenance requirements can lead to the selection of specialized pumps like screw and rotary pumps, each offering distinct advantages tailored to particular oil processing needs. By carefully evaluating these factors, operators can ensure that they select the most suitable pump type for their specific oil-related applications, ultimately enhancing their overall efficiency and performance.
Maintenance Tips to Enhance Oil Pump Longevity and Efficiency
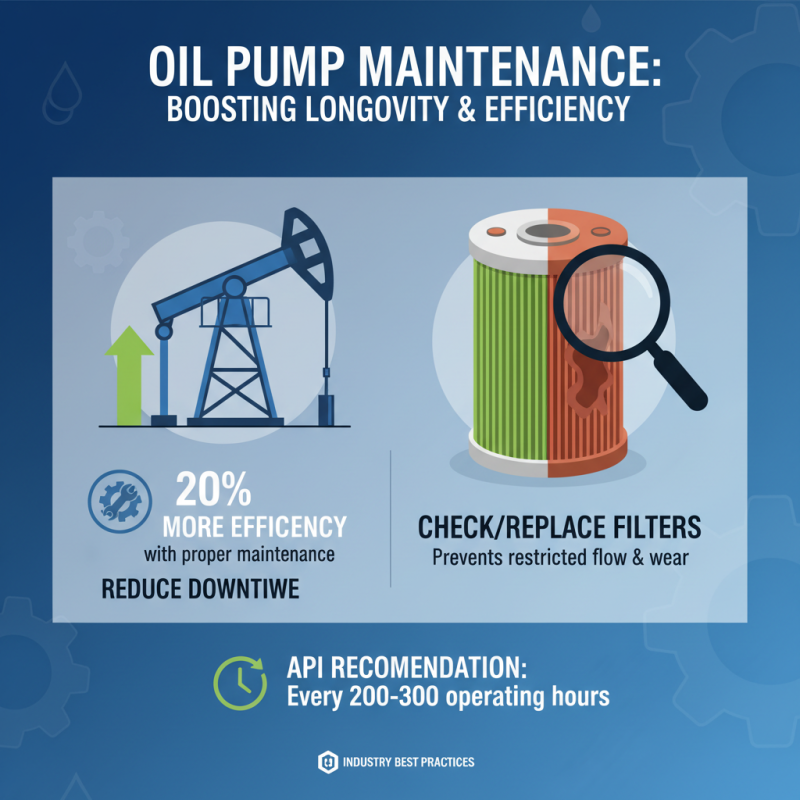
Proper maintenance of oil pumps is crucial for maximizing their longevity and efficiency, as evidenced by industry reports indicating that well-maintained pumps can operate up to 20% more efficiently. Regular maintenance can significantly reduce the risk of breakdowns, which not only prolongs the equipment's lifespan but also minimizes costly downtimes. One of the most vital maintenance practices is to regularly check and replace filters. Clogged filters can restrict oil flow, leading to increased wear and tear on the pump components. The American Petroleum Institute (API) suggests that routine filter inspections should occur every 200 to 300 operating hours to ensure optimal performance.
Additionally, monitoring the lubrication and coolant levels is essential in enhancing the performance of oil pumps. Studies show that inadequate lubrication can lead to friction and overheating, which are primary causes of failure in pump systems. It is recommended to follow the manufacturer’s specifications regarding lubricant types and change intervals, typically every 1,000 hours of operation. Regularly inspecting seals and gaskets for wear and leaks also plays a vital role in maintaining efficiency. The Global Pump Industry Report highlights that leaks can result in significant oil loss, potentially compromising operational efficiency by up to 15%. Implementing these maintenance tips can lead to substantial improvements in the efficiency and reliability of oil pumps, ultimately benefiting overall operational sustainability.
Related Posts
-

Top 10 Essential Pumps for Oil: Your Ultimate Buying Guide
-

How to Choose the Right Pumps for Oil Based on Your Specific Needs
-
Why You Should Choose Air Oil Pumps for Your Industrial Needs Today
-
The Essential Role of Lubrication Pumps in Enhancing Equipment Lifespan and Efficiency
-
Unlocking Efficiency: The Essential Guide to Choosing the Right Lube Oil Pump for Your Equipment
-
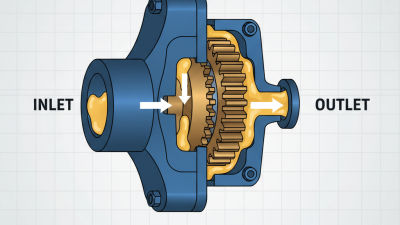
Understanding the Mechanism of Lube Pumps: A Comprehensive Guide for Efficient Lubrication Systems